Galaxy-cluster-stacked Fermi-LAT II: extended central hadronic signal
Galaxy-cluster-stacked Fermi-LAT II: extended central hadronic signal
Uri Keshet
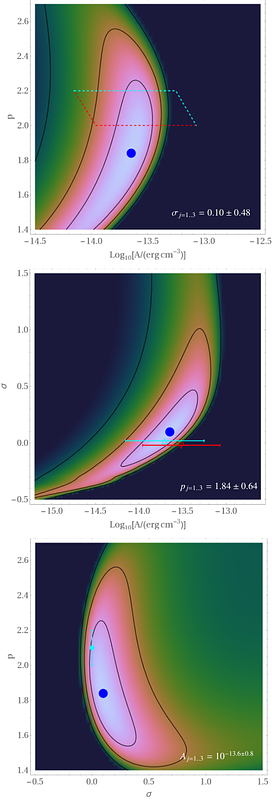
AbstractFaint $\gamma$-ray signatures emerge in Fermi-LAT data stacked scaled to the characteristic $\theta_{500}$ angles of MCXC galaxy clusters. After Paper I of this series thus discovered virial shocks, later supported in other bands, this second paper focuses on cluster cores. Stacking $1$-$100$ GeV source-masked data around clusters shows a significant ($4.7\sigma$ for 75 clusters) and extended central excess, inconsistent with central point sources. The resolved signal is best fit ($3.7\sigma$ TS-test) as hadronic emission from a cosmic-ray ion (CRI) distribution that is flat both spectrally ($p\equiv1-d\ln u/d\ln E=2.0\pm0.3$) and spatially (CRI-to-gas index $\sigma=0.1\pm0.4$), carrying an energy density $du(0.1\theta_{500})/d\ln E=10^{-13.6\pm0.5}$ erg cm$^{-3}$ at $E=100$ GeV energy; insufficient resolution would raise $p$ and $\sigma$. Such CRI match the long-predicted distribution needed to power diffuse intracluster radio emission in its various forms (mini-halos, giant halos, standard relics, their transitional forms, and mega-halos), disfavoring models that invoke electron (re)acceleration in weak shocks or turbulence. Stringent upper limits on residual $\gamma$-ray emission, e.g. from dark-matter annihilation, are imposed.