Search for High Energy Neutrino Sources using IceCube Neutrino Events and \textit{Fermi}/LAT Observations
Search for High Energy Neutrino Sources using IceCube Neutrino Events and \textit{Fermi}/LAT Observations
Rajendra Neupane, Niraj Dhital
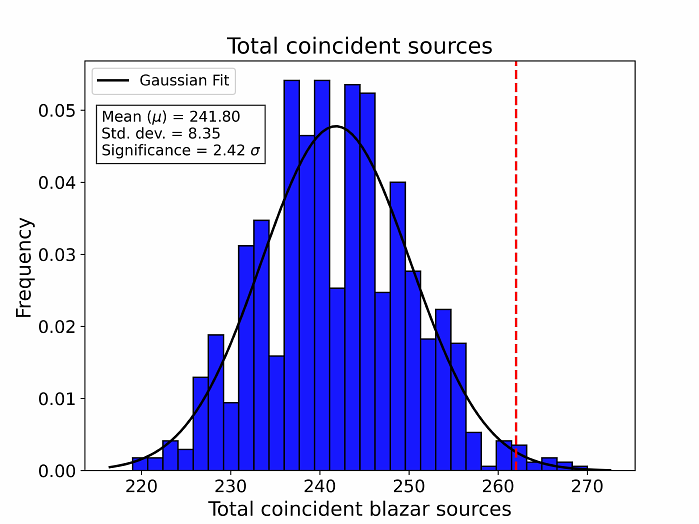
AbstractContext. The sources of high-energy astrophysical neutrinos remain largely unknown. Multi-wavelength observational campaignshave identified a few plausible candidates, but their numbers are limited. Aims. We search for an excess of high-energy neutrino events originating from the directions of blazar sources, compared to the expected background. Additionally, we investigate blazars located within a small angular distance from the arrival directions of high-energy neutrinos, analyzing their characteristics to assess their plausibility as neutrino sources. Methods. We generate random samples of events following the right ascension and the declination distributions of the high-energy neutrino events detected by the IceCube Neutrino Observatory and count the coincidences of generated samples as well as the true observations with the Fermi-LAT blazar sources. Furthermore, we conduct temporal analysis of gamma-ray light curves and spectral analysis of blazar sources with the highest clustering of neutrino events. Results. We find an excess of high-energy neutrino events from the directions of Fermi blazars beyond random coincidence, with a significance of 2.42$\sigma$. Among the nine blazars which have a maximum number of neutrino events (four) arriving from within 3 degrees from them, 4FGL J1012.3+0629 exhibits the most significant variability around the neutrino detection time. Our study identifies 4FGL J1012.3+0629, 4FGL J2118.0+0019, 4FGL J2226.8+0051 and 4FGL J2227.9+0036 as plausible high-energy neutrino source candidates. The neutrino events IC110726A, IC170308A, IC190415A, IC141210A, IC150102A, IC230524A, IC140114A, IC110807A, and IC200523A likely originate from these sources. Additionally, we find that the spectral index tends to harden when these high-energy neutrino events are detected.