Constraining first-order phase transition inside neutron stars with application of Bayesian techniques on PSR J0437-4715 NICER data
Constraining first-order phase transition inside neutron stars with application of Bayesian techniques on PSR J0437-4715 NICER data
Chun Huang, Shashwat Sourav
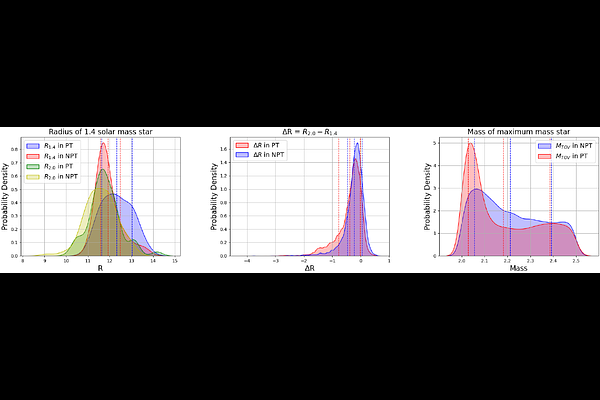
AbstractUnderstanding the existence of exotic matter phases and phase transitions within the core of neutron stars is crucial to advancing our knowledge of cold-dense matter physics. Recent multi-messenger observations, including gravitational waves from neutron star mergers and precise X-ray data from NASA's Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) mission, have significantly constrained the neutron star equation of state (EOS). This study investigates the effects of phase transitions in neutron stars, focusing on NICER's latest observation of PSR J0437-4715. We employ Bayesian inference techniques to evaluate the presence of first-order phase transitions using a piecewise polytropic EOS model. Our analysis incorporates data from multiple NICER sources, to refine constraints on key phase transition parameters, including critical density and transition depth. We find that including data from PSR J0437-4715 improves the evidence of phase transitions and tightens the EOS constraints, especially at higher densities. However, Bayes factor analysis only indicates a slight preference for models without phase transitions and current observational precision is insufficient to draw definitive conclusions. In particular, this polytropic model identifies the critical phase transition mass of neutron stars as being close to 1.4 solar masses, which coincides with the approximate mass range of PSR J0437-4715. This work emphasizes the importance of precise measurements of PSR J0437-4715 for deepening our understanding of neutron star interiors and exploring potential new physics at extreme densities.