On the origin of mid-infrared colors in $γ$-ray blazars
On the origin of mid-infrared colors in $γ$-ray blazars
Raniere de Menezes, Raffaele D'Abrusco, Francesco Massaro
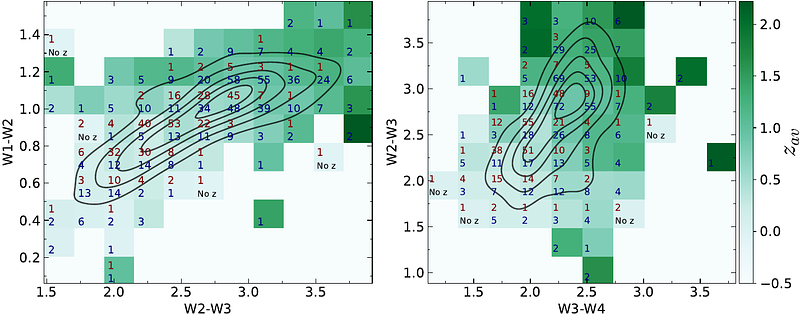
AbstractContext. The combination between non-thermal and thermal emission in $\gamma$-ray blazars pushes them to a specific region of the mid-infrared three-dimensional color diagram, the so-called blazar locus, built based on observations performed with the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer. The selection of blazar candidates based on these mid-infrared colors has been extensively used in the past decade in the hunt for the counterparts of unassociated $\gamma$-ray sources observed with the Fermi Large Area Telescope and in the search for new blazars in optical spectroscopic campaigns. Aims. In this work, we provide a theoretical description of the origin of the blazar locus and show how we can reasonably reproduce it with a model consisting of only three spectral components: a log-parabola accounting for the non-thermal emission, and an elliptical host and dust torus accounting for the thermal emission. Methods. We simulate spectral energy distributions for blazars, starting with a pure log-parabola model and then increasing its complexity by adding a template elliptical galaxy and dust torus. From these simulations, we compute the mid-infrared magnitudes and corresponding colors to create our own version of the blazar locus. Results. Our modeling allows for the selection of spectral parameters that better characterize the mid-infrared emission of $\gamma$-ray blazars, such as the log-parabola curvature ($\beta < 0.04$ for 50\% of our sample) and an average spectral peak around $E_p \approx 1.5 \times 10^{-13}$ erg. We also find that the log-parabola is the main spectral component behind the observed mid-infrared blazar colors, although additional components such as a host galaxy and a dust torus are crucial to obtain a precise reconstruction of the blazar locus.