A novel experimental approach to uncover the nature of cosmic-ray Deuterium
A novel experimental approach to uncover the nature of cosmic-ray Deuterium
Francesco Dimiccoli, Francesco Maria Follega
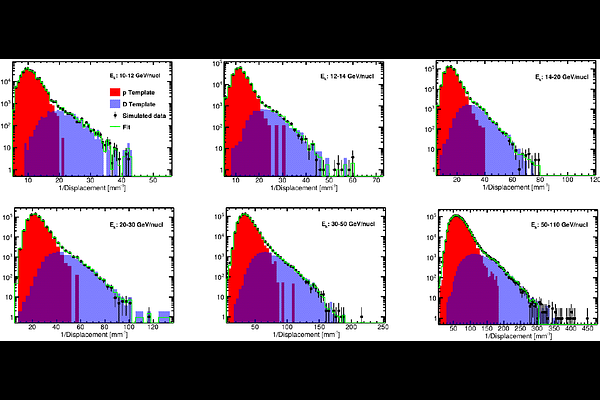
AbstractStudying the isotopic composition of cosmic-rays (CRs) provides crucial insights into the galactic environment and helps improve existing propagation models. Special attention is given to the secondary-to-primary ratios of light isotopic components in CRs, as these measurements can offer complementary data compared to traditional secondary-to-primary ratios like B/C. Recently, a precision measurement of the Deuterium (D) abundance in CR in the 2-21 GV rigidity range provided by the AMS02 experiment unexpectedly detected an excess of D with respect to its expected secondary nature, opening the field for new measurements at high rigidity to determine how the spectrum evolves and whether there is confirmation of a primary or primary plus secondary origin. While there are theoretical models that attempt to explain this excess, the experimental uncertainties on D production cross-sections and on CR propagation models remain significant, and only new and precise measurements can dissipate existing doubts. In this work we review the current experimental scenario and we propose a dedicated experiment able to extend the D abundance measurement up to 100 GeV/nucl without the need of a magnetic spectrometer, using a multiple scattering based technique for the measurement of particle momentum. The expected performances of the proposed detector were assessed through a dedicated simulation using the GEANT4 package, and its role in the current particle physics scenario is discussed.