The Hidden Threat in Plain Text: Attacking RAG Data Loaders
The Hidden Threat in Plain Text: Attacking RAG Data Loaders
Alberto Castagnaro, Umberto Salviati, Mauro Conti, Luca Pajola, Simeone Pizzi
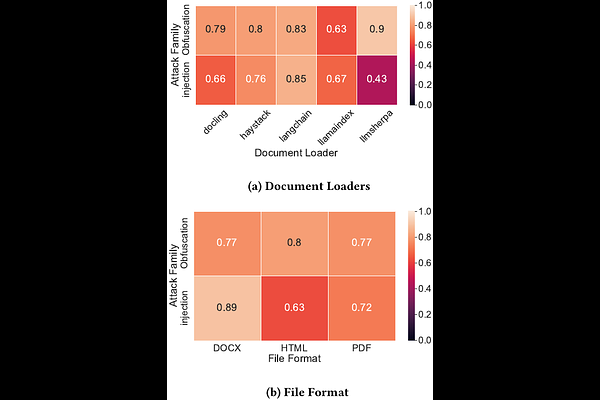
AbstractLarge Language Models (LLMs) have transformed human-machine interaction since ChatGPT's 2022 debut, with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) emerging as a key framework that enhances LLM outputs by integrating external knowledge. However, RAG's reliance on ingesting external documents introduces new vulnerabilities. This paper exposes a critical security gap at the data loading stage, where malicious actors can stealthily corrupt RAG pipelines by exploiting document ingestion. We propose a taxonomy of 9 knowledge-based poisoning attacks and introduce two novel threat vectors -- Content Obfuscation and Content Injection -- targeting common formats (DOCX, HTML, PDF). Using an automated toolkit implementing 19 stealthy injection techniques, we test five popular data loaders, finding a 74.4% attack success rate across 357 scenarios. We further validate these threats on six end-to-end RAG systems -- including white-box pipelines and black-box services like NotebookLM and OpenAI Assistants -- demonstrating high success rates and critical vulnerabilities that bypass filters and silently compromise output integrity. Our results emphasize the urgent need to secure the document ingestion process in RAG systems against covert content manipulations.