Generative Agents: Interactive Simulacra of Human Behavior
Generative Agents: Interactive Simulacra of Human Behavior
Joon Sung Park, Joseph C. O'Brien, Carrie J. Cai, Meredith Ringel Morris, Percy Liang, Michael S. Bernstein
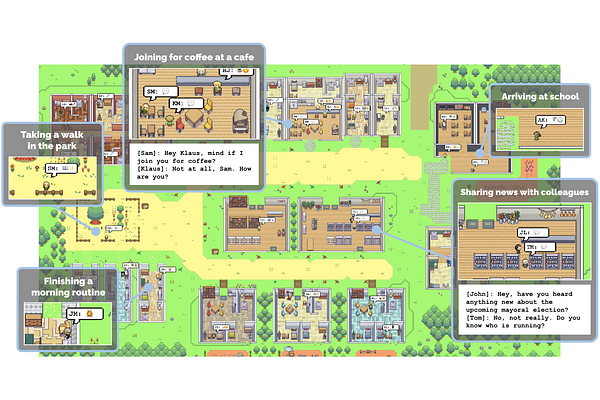
AbstractBelievable proxies of human behavior can empower interactive applications ranging from immersive environments to rehearsal spaces for interpersonal communication to prototyping tools. In this paper, we introduce generative agents--computational software agents that simulate believable human behavior. Generative agents wake up, cook breakfast, and head to work; artists paint, while authors write; they form opinions, notice each other, and initiate conversations; they remember and reflect on days past as they plan the next day. To enable generative agents, we describe an architecture that extends a large language model to store a complete record of the agent's experiences using natural language, synthesize those memories over time into higher-level reflections, and retrieve them dynamically to plan behavior. We instantiate generative agents to populate an interactive sandbox environment inspired by The Sims, where end users can interact with a small town of twenty five agents using natural language. In an evaluation, these generative agents produce believable individual and emergent social behaviors: for example, starting with only a single user-specified notion that one agent wants to throw a Valentine's Day party, the agents autonomously spread invitations to the party over the next two days, make new acquaintances, ask each other out on dates to the party, and coordinate to show up for the party together at the right time. We demonstrate through ablation that the components of our agent architecture--observation, planning, and reflection--each contribute critically to the believability of agent behavior. By fusing large language models with computational, interactive agents, this work introduces architectural and interaction patterns for enabling believable simulations of human behavior.