Scattering of stellar-mass black holes and gravitational wave bremsstrahlung radiation in AGN disks
Scattering of stellar-mass black holes and gravitational wave bremsstrahlung radiation in AGN disks
Peter Lott, Christian Faulhaber, Joshua Brandt, Gongjie Li, Hareesh Bhaskar, Laura Cadonati
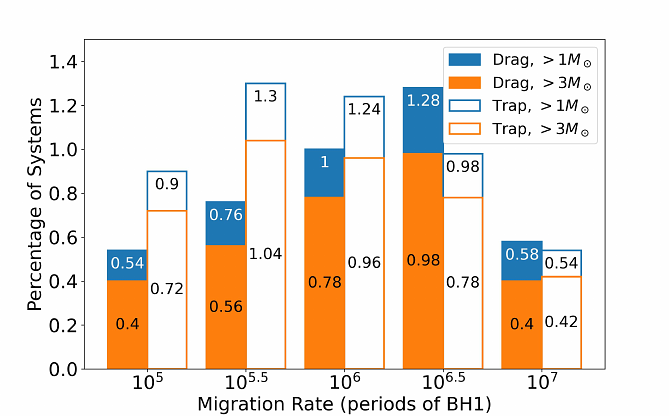
AbstractDynamics of stellar mass black holes (sBHs) embedded in active galactic nuclei (AGNs) could produce highly eccentric orbits near the central supermassive black hole, leading to repeated close encounters that emit gravitational waves in the LIGO frequency band. Many works have focused on the mergers of sBH in the disk that produce gravitational waves; however, sBHs in hyperbolic orbits also emit gravitational-wave \bremss{} that can be detected by ground-based interferometers like LIGO. In this work, we analyze the scattering of sBHs in an AGN disk as they migrate inside the disk, focusing on gravitational-wave \bremss{} emission. We determine how the gravitational-wave emission depends on the different parameters of the scattering experiments, such as the mass of the supermassive black hole and the sBH migration rate and mass ratio. We find that scattering with detectable gravitational-wave \bremss{} is more frequent around lower mass SMBHs ($\sim 10^{5-6}$M$_\odot$). We then conduct a suite of Monte Carlo simulations and estimated the rate for ground-based gravitational-wave detections to be in the range of 0.08 - 1194 $\text{Gpc}^{-3} \text{ yr}^{-1}$, depending on migration forces and detection thresholds, with large uncertainties accounting for variations in possible AGN environments. The expected rate for our {\tt Fiducial} parameters is 3.2 $\text{Gpc}^{-3} \text{ yr}^{-1}$. Finally, we provide first-principle gravitational wave templates produced by the encounters.