Radio emission across the entire rotation phases of pulsars
Radio emission across the entire rotation phases of pulsars
P. F. Wang, J. L. Han
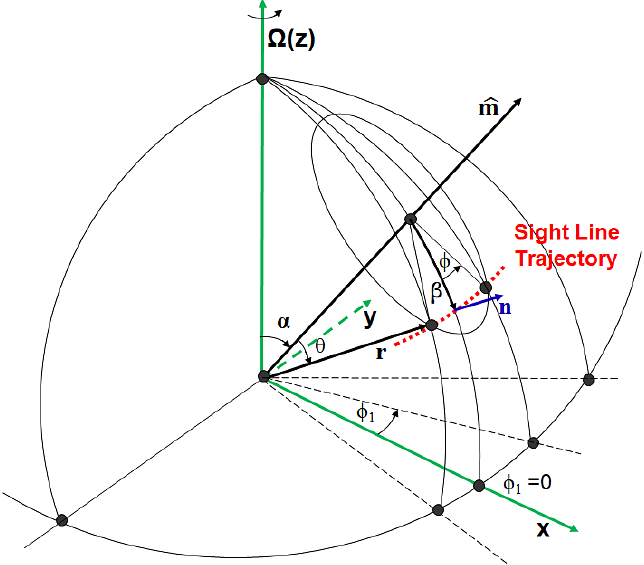
AbstractSuper-sensitive observations of bright pulsars by the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) have revealed weak radio emission continuously emerged in the rotation phases between the main pulse and interpulse of an rotating neutron star. We develop a model for the polarized radio emission radiated from different heights in the pulsar magnetosphere and examine emission intensity distribution over the whole rotation phases of pulsars seen from all directions by the line of sight. We find that for pulsars with small periods and the magnetosphere filled with much more relativistic particles, the polarized radio emission can be generated in all rotation phases for both the aligned and perpendicular rotating neutron stars. When the line of sight cuts the pulsar emission beam between the rotation and magnetic axes, the polarization angles have the same sense of variation gradient for the ``main'' pulse and ``interpulse''. If the line of sight cuts the beams between the inclined magnetic axis and the equator, the opposite senses can be found for the main pulse and interpulse. In addition to the pulsed emission, we find persistent radio emission generated in the pulsar magnetosphere. The model can naturally explain the emission across the entire rotation phases.