X-ray observations of Nova Sco 2023: Spectroscopic evidence of charge exchange
X-ray observations of Nova Sco 2023: Spectroscopic evidence of charge exchange
Sharon Mitrani, Ehud Behar, Marina Orio, Jack Worley
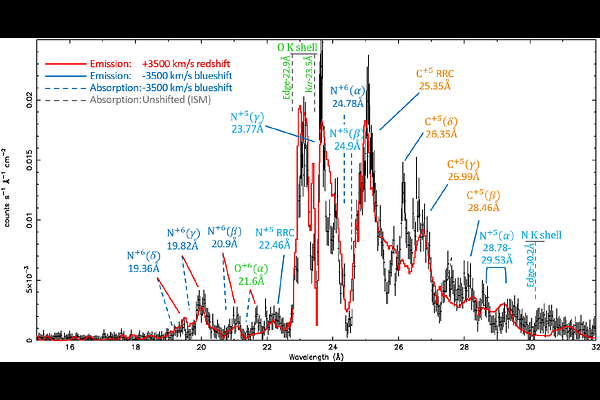
AbstractThe super-soft source (SSS) phase of a nova eruption, observed a few days after the outburst, usually displays an absorbed X-ray thermal continuum with absorption features, emitted by the white dwarf (WD) atmosphere. However, the X-ray spectra of many novae in this phase display additional emission lines which likely originate from shocks in the novae ejecta. When the shocked plasma interacts with cold gas, narrow radiative recombination continua (RRCs) and charge exchange (CX) emission are observed. We present the analysis of high-resolution ChandraLETG X-ray grating spectra of Nova Sco 2023, observed 128 and 183 days after the optical peak, on 2023 August and October. At both epochs, the absorbed X-ray thermal continuum is well described by a Non-Local Thermal Equilibrium atmosphere model with a temperature T=750,000 K (kT = 65 eV). On day 128, the atmosphere is found to be outflowing at v=-3500 km s^-1. On day 183, the atmosphere brightened by a factor of ~2 and slowed down to v=-1500$ km s^-1. The discrete emission features of the spectrum consist of the C^+5, N^+5, and N^+6 RRCs, indicating a cold electron temperature of kT_e=1 eV on day 128, and kT_e=20 eV on day 183. The observed line series of H-like and He-like C^+5, N^+5, N^+6, and O^+6 show enhanced intensities of high-n (principal quantum number) transitions, consistent with a CX model of hot ions at kT~100 eV. The velocity shift of the CX lines remained at v=+-3000 km s^-1, which can be explained by a bipolar outflow. After Nova Ret 2020 (YZ Ret), Nova Sco 2023 is yet another nova in which we have found exquisite evidence of CX in astrophysical ionized plasma.