Revealing the nature of ultra-long period objects with space-based gravitational-wave interferometers
Revealing the nature of ultra-long period objects with space-based gravitational-wave interferometers
Arthur G. Suvorov, Clara Dehman, José A. Pons
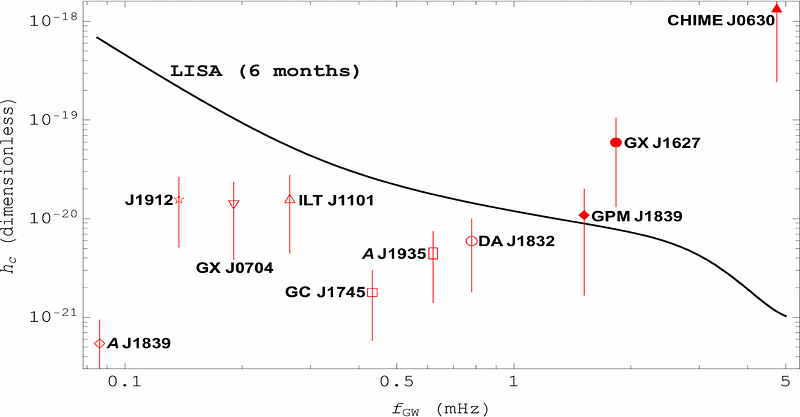
AbstractA few members of the recently-discovered class of ultra-long period objects have been identified as binaries with white-dwarf primaries. In most cases however, electromagnetic data are inconclusive and isolated magnetars remain a viable candidate. If the pulsation period matches that of the orbit though -- as is the case for ILT J1101+5521 and GLEAM-X J0704-37 -- several of these elusive radio transients should be gravitational-wave bright in the mHz band. Space-based interferometers could thus be used to provide independent constraints on their nature. We quantify the signal-to-noise ratio for the known systems, assuming they are compact binaries, and show that a few should be detectable with only a few months of data folding. Astrophysical implications for (non-)detections are discussed.