Spatially resolved H$α$ emission in B14-65666: compact starbursts, ionizing efficiency and gas kinematics in an advanced merger at the Epoch of Reionization
Spatially resolved H$α$ emission in B14-65666: compact starbursts, ionizing efficiency and gas kinematics in an advanced merger at the Epoch of Reionization
C. Prieto-Jiménez, J. Álvarez-Márquez, L. Colina, A. Crespo Gómez, A. Bik, G. Östlin, A. Alonso-Herrero, L. Boogaard, K. I. Caputi, L. Costantin, A. Eckart, M. García-Marín, S. Gillman, J. Hjorth, E. Iani, I. Jermann, A. Labiano, D. Langeroodi, J. Melinder, T. Moutard, F. Peißker, P. G. Pérez-González, J. P. Pye, P. Rinaldi, T. V. Tikkanen, P. van der Werf, F. Walter, T. Hashimoto, Y. Sugahara, M. Güdel, T. Henning
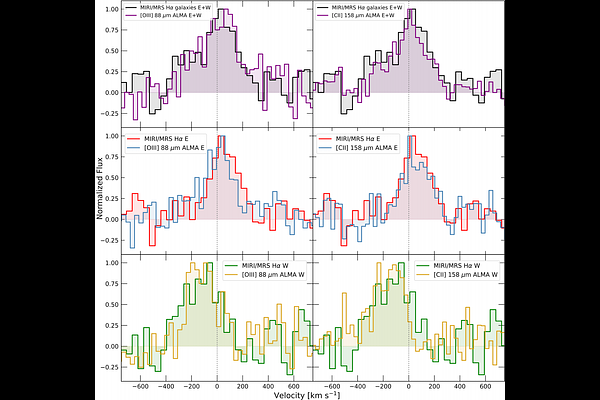
AbstractWe present MIRI/JWST medium resolution spectroscopy (MRS) and imaging (MIRIM) of B14-65666, a Lyman-break and interacting galaxy at redshift $z$=7.15. We detect the H$\alpha$ line emission in this system, revealing a spatially-resolved structure of the H$\alpha$ emitting gas, which consists of two distinct galaxies, E and W, at a projected distance of 0.4". Galaxy E is very compact in the rest-frame UV, while W galaxy is more extended, showing a clumpy structure reminiscent of a tidal tail. The total H$\alpha$ luminosity implies that the system is forming stars at a Star Formation Rate (SFR) of 76$\pm$8 M$_{\odot}$ yr$^{-1}$ and 30$\pm$4 M$_{\odot}$ yr$^{-1}$ for E and W, respectively. The ionizing photon production efficiency is within the range measured in galaxies at similar redshifts. The high values derived for the H$\alpha$ equivalent widths (EW) and the distinct locations of the E and W galaxies in the $\log(\zeta_\mathrm{ion}$) $-$ EW (H$\alpha$) plane, indicate that the system is dominated by a young (less than 10 Myr) stellar population. The overall spectral energy distribution suggests that in addition to a young stellar population, the two galaxies may have mature stellar population and very different dust attenuation. The derived SFR and stellar masses identify the two galaxies as going through a starburst phase. The kinematics of the ionized gas traced by the H$\alpha$ line show a velocity difference of 175 $\pm$ 28 km s$^{-1}$ between the two components of B14-65666. The in-depth study of systems like B14-65666 reveal how galaxy mergers in the early Universe drive intense star formation, shape the interstellar medium, and influence the buildup of stellar mass, just 700 $-$ 800 Myr after the Big Bang.