Spectropolarimetric Evolution of SN 2023ixf: an Asymmetric Explosion in a Confined Aspherical Circumstellar Medium
Spectropolarimetric Evolution of SN 2023ixf: an Asymmetric Explosion in a Confined Aspherical Circumstellar Medium
Sergiy S. Vasylyev, Luc Dessart, Yi Yang, Alexei V. Filippenko, Kishore C. Patra, Thomas G. Brink, Lifan Wang, Ryan Chornock, Raffaella Margutti, Elinor L. Gates, Adam J. Burgasser, Huei Sears, Preethi R. Karpoor, Natalie LeBaron, Emma Softich, Christopher A. Theissen, Eli Wiston, WeiKang Zheng
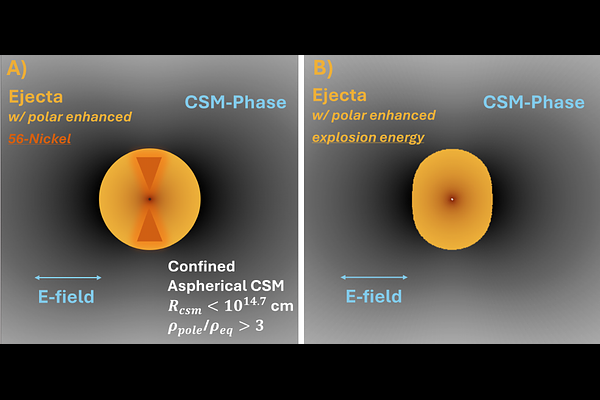
AbstractWe present complete spectropolarimetric coverage of the Type II supernova (SN) 2023ixf ranging from 1 to 120 days after explosion. Polarimetry was obtained with the Kast double spectrograph on the Shane 3m telescope at Lick Observatory. As the ejecta interact with circumstellar material (CSM) during the first week, the intrinsic polarization of SN 2023ixf is initially high at $\lesssim$1%, dropping steeply within days down to $\sim$ 0.4% when the ejecta sweep up the optically-thick CSM. The continuum polarization stays low at $\sim$ 0.2% thereafter, until it rises again to $\sim$ 0.6% as the ejecta transition to the nebular phase. We model this evolution using a combination of archival and newly-computed 2D polarized radiative-transfer models. In this context, we interpret the early-time polarization as arising from an aspherical CSM with a pole-to-equator density contrast $\gtrsim$ 3. We propose that the surge in polarization at late times originates from an asymmetric distribution of $^{56}$Ni deep in the ejecta. The distinct sources of asymmetries at early and late times are consistent with the temporal evolution of the observed polarization and the polarization angle in SN 2023ixf.