Galaxy And Mass Assembly (GAMA): from filaments to voids, how extreme environment affects gas metallicity and SFR in galaxies
Galaxy And Mass Assembly (GAMA): from filaments to voids, how extreme environment affects gas metallicity and SFR in galaxies
J. A. Molina-Calzada, M. A. Lara-López, J. Gallego, A. M. Hopkins, Benne W. Holwerda, A. R. López-Sánchez
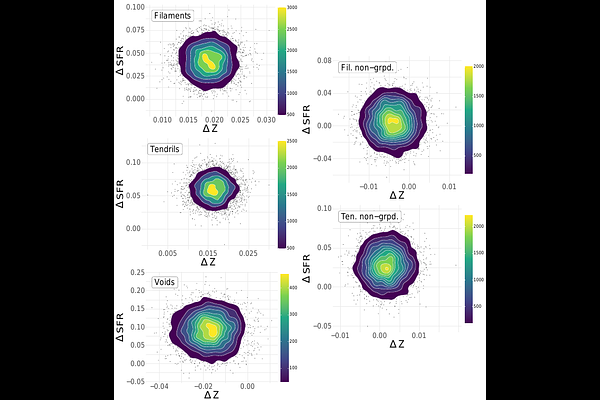
AbstractWe analyse the stellar mass-metallicity (M-Z) and stellar mass-star formation rate (M-SFR) relations for star-forming galaxies classified by their environment and compare them with matched control samples of field galaxies. Using data from the Galaxy And Mass Assembly (GAMA) survey and the filament catalogue, which categorises galaxies into filaments, tendrils, and voids, we correct emission lines for dust extinction and select star-forming galaxies based on the BPT diagram. Metallicity and star formation rate are estimated and used to fit the M-Z and M-SFR relations through both Bayesian and least-squares approaches. We find that metallicity increases in denser environments, while star formation rate decreases, with the most notable contrasts seen between filament/tendril galaxies and those in voids. Galaxies in filaments and tendrils that are not group members show little to no deviation from their control samples. Morphological analysis reveals no significant differences. Overall, galaxies in denser environments appear more chemically enriched with lower SFRs, likely due to processed material and reduced cold gas availability, while isolated void galaxies maintain higher SFRs and lower metallicities, possibly due to ongoing cold gas accretion. These results suggest that local environmental conditions, rather than large-scale structure alone, are the main drivers of the observed trends.