Detection of X-ray Polarization in the Hard State of IGR J17091-3624: Spectro-Polarimetric Study with IXPE and NuSTAR Data
Detection of X-ray Polarization in the Hard State of IGR J17091-3624: Spectro-Polarimetric Study with IXPE and NuSTAR Data
Dipak Debnath, Subham Srimani, Hsiang-Kuang Chang
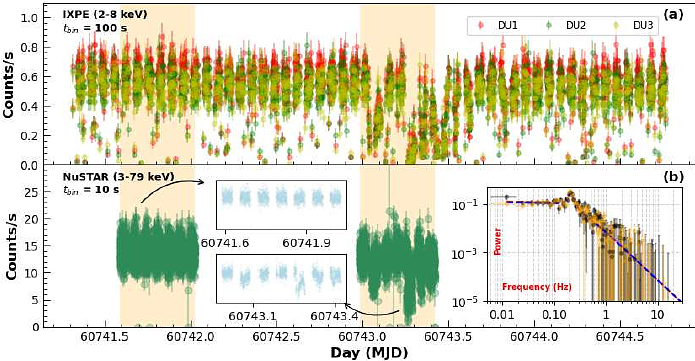
AbstractThe class-transition Galactic X-ray binary IGR J17091--3624 was simultaneously monitored by the IXPE and NuSTAR satellites. We present a detailed spectro-polarimetric study of the source using data from both satellites covering the period from March 7-10, 2025. A polarimetric analysis in the $2$-$8$~keV band using a model-independent method reveals a significant detection of polarization degree (PD) of $(11.3\pm2.35)\%$ at a polarization angle (PA) of $82^\circ.7\pm5^\circ.96$ (significant at $>4\sigma$). The model-dependent polarization analysis using the polconst and polpow models yields consistent values of PD and PA. In both methods, an energy-dependent increasing trend of PD is observed. In the $6$-$8$~keV band, a maximum PD of $(29.9\pm8.46)\%$ is detected at a PA of $88^\circ.0\pm8^\circ.15$ (significant at $>3\sigma$) . The joint spectral analysis using IXPE and NuSTAR data in the $2$-$70$~keV band was performed with four different sets of phenomenological and physical models. Our results indicate a strong dominance of non-thermal photons originating from a `hot' Compton cloud, suggesting that the source was in a hard spectral state. Spectral fitting with the physical kerrbb and TCAF models provides an estimate of the black hole mass $M_{\rm BH} = 14.8^{+4.7}_{-3.4}~M_\odot$ and dimensionless spin parameter $a^* \sim 0.54$.