Hadronic origin of the very high-energy gamma-ray emission from the low-luminosity AGN in NGC 4278
Hadronic origin of the very high-energy gamma-ray emission from the low-luminosity AGN in NGC 4278
Asahi Shoji, Yutaka Fujita, Norita Kawanaka, Susumu Inoue, Kosuke Nishiwaki
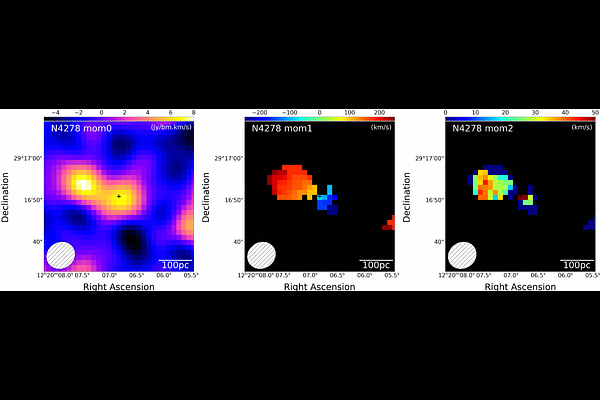
AbstractThe Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory has detected very high-energy (VHE) gamma rays from NGC 4278, which is known to host a low-luminosity active galactic nucleus (AGN). Having only very weak radio jets, the origin of its VHE gamma rays is unclear. In this paper we first show that NGC 4278 has a massive molecular cloud surrounding the nucleus by analyzing data taken with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array. We then assume that cosmic ray protons are accelerated in a radiatively inefficient accretion flow around the supermassive black hole, which diffuse into the molecular cloud and produce gamma rays and neutrinos via $pp$ interactions. We model the gamma-ray spectra and find that the observations can be explained by such hadronic processes if the AGN activity was higher in the past than at present, and the diffusion coefficient in the molecular cloud is appreciably smaller than in the Milky Way interstellar medium. However, we also show that the high-energy neutrinos co-produced with the gamma rays are unlikely to be detectable even with IceCube-Gen2.