Parity-violating scalar trispectrum from helical primordial magnetic fields
Parity-violating scalar trispectrum from helical primordial magnetic fields
Kaito Yura, Shohei Saga, Maresuke Shiraishi, Shuichiro Yokoyama
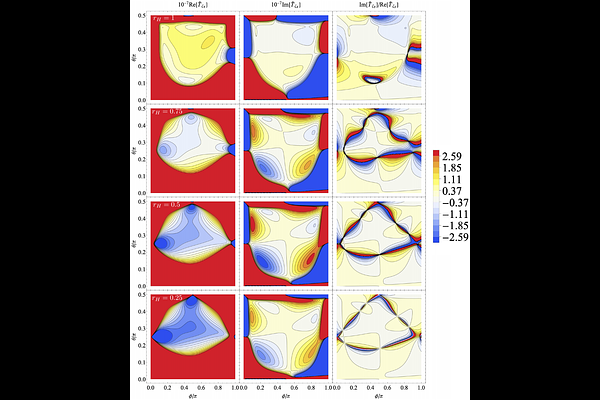
AbstractWe investigate primordial magnetic fields (PMFs) as a potential source of the parity-violating signatures recently implied by observations of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) anisotropies and the large-scale structure of the Universe. Among various possibilities, helical PMFs are of particular interest, as they inherently violate parity symmetry and can explain the observed magnetic fields, especially in void regions. PMFs, if generated in the early universe, can source curvature perturbations, which evolve into the present density fluctuations observed in galaxy surveys. Motivated by this, we focus on the imprint of helical PMFs on the trispectrum of the sourced primordial curvature perturbations, a leading-order statistics sensitive to parity-violating signals in three-dimensional space. We derive the analytic expressions for the trispectrum of the primordial curvature perturbations sourced by taking into account both the helical and non-helical PMFs and analytically reduce their expressions by using the pole approximation, whose validity is confirmed by comparison with the exact results. We find that, varying the ratio of the amplitude of the helical to non-helical power spectrum, the structure of the trispectrum qualitatively changes, particularly the ratio of the imaginary to real components of the trispectrum. Our findings highlight the primordial trispectrum as a promising probe of cosmological parity violation in the early universe and provide a theoretical basis for future precise observations of higher order statistics in the CMB anisotropies and the galaxy clustering.