A Theoretical Three-Dimensional Diagram to Separate Star Formation, Active Galactic Nuclei, and Shocks in Galaxies
A Theoretical Three-Dimensional Diagram to Separate Star Formation, Active Galactic Nuclei, and Shocks in Galaxies
Peixin Zhu, Lisa J. Kewley, Ralph S. Sutherland, Kathryn Grasha
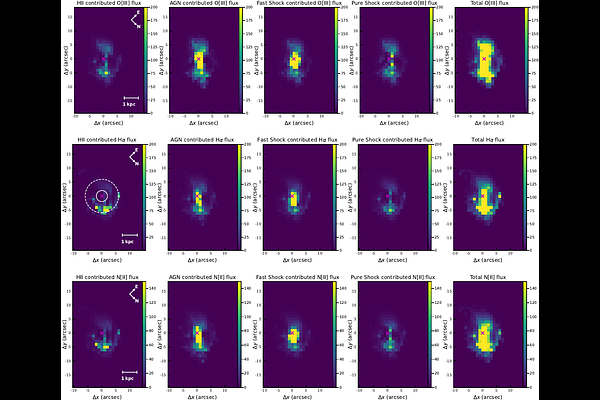
AbstractThe excitation sources in galaxies are frequently mixed due to AGN and stellar feedback, including star formation, active galactic nuclei (AGNs), and shock excitation. Disentangling the star formation, AGN, and shocks in galaxy integral-field spectra (IFU) at optical wavelengths is crucial to expanding the galaxy sample for AGN and stellar feedback studies, given the lack of multiwavelength observations for most of the galaxies that are observed in optical wavelengths. Previous methods to address this issue either have a limited application range or are highly uncertain in separating AGN from shock excitation (D'Agostino et al. 2019; Johnston et al. 2023). Here, we propose a theoretical three-dimensional (3D) diagram. This theoretical 3D diagram overcomes the limitations of previous methods and can simultaneously separate star formation, AGNs, and shocks in active galaxies. Along with the separation, the new theoretical 3D diagram also constrains the gas metallicity, ionization parameter, and gas pressure within the galaxy. By applying the Very Large Telescope (VLT)/MUSE IFU data and the Wide Field Spectrograph IFU data for NGC5728 on the theoretical 3D diagram, we find a star-forming ring surrounding the galaxy center with a projected radius of $\sim$1 kpc in the sky plane, an AGN ionized-bicone extended up to $\sim$2 kpc from the nuclear center, and a fast shock dominated disk region at the base of the AGN outflow, which is likely associated with a nuclear accretion disk or a result of jet-ISM interaction. The theoretical 3D diagram opens a new window to study the interplay among star formation, AGN, and shocks in active galaxies.