gwharmone: first data-driven surrogate for eccentric harmonics in binary black hole merger waveforms
gwharmone: first data-driven surrogate for eccentric harmonics in binary black hole merger waveforms
Tousif Islam, Tejaswi Venumadhav, Ajit Kumar Mehta, Isha Anantpurkar, Digvijay Wadekar, Javier Roulet, Jonathan Mushkin, Barak Zackay, Matias Zaldarriaga
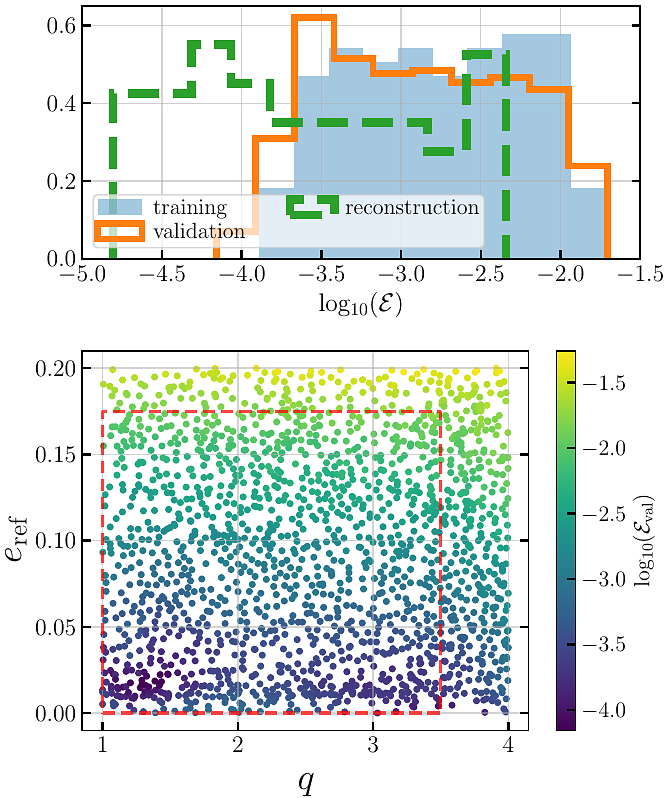
AbstractWe present gwharmone, the first data-driven surrogate model for eccentric harmonics (as well as the full radiation content) of the dominant quadrupolar mode in eccentric, non-spinning binary black hole mergers. Our model is trained on 173 waveforms, each $100,000M$ long (where $M$ is the total mass), generated for mass ratios $q \in [1,3.5]$ and eccentricities $e_{\rm ref} \in [0,0.2]$ (at the start of the waveform). The eccentric harmonics are extracted from the effective-one-body waveforms using the \texttt{gwMiner} package. We apply a singular value decomposition (SVD) to obtain a set of reduced basis vectors, necessary to construct a lower-dimensional representation of data, and use Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) to interpolate SVD coefficients across parameter space, allowing for prediction at new parameter points. The model includes the effect of mean anomaly, its evaluation cost is only $\sim 0.1$ second and it achieves an average time-domain (validation) error of ~0.001 and frequency-domain (validation) mismatches below 0.01 for advanced LIGO sensitivity. Our model can therefore be useful in efficient searches and parameter estimation of eccentric mergers. gwharmone will be publicly available through the gwModels package.