Chemical Abundances in the Nuclear Star Cluster of the Milky Way: alpha-Element Trends and Their Similarities with the Inner Bulge
Chemical Abundances in the Nuclear Star Cluster of the Milky Way: alpha-Element Trends and Their Similarities with the Inner Bulge
N. Ryde, G. Nandakumar, M. Schultheis, G. Kordopatis, P. di Matteo, M. Haywood, R. Schödel, F. Nogueras-Lara, R. M. Rich, B. Thorsbro, G. Mace, O. Agertz, A. M. Amarsi, J. Kocher, M. Molero, L. Origlia, G. Pagnini, E. Spitoni
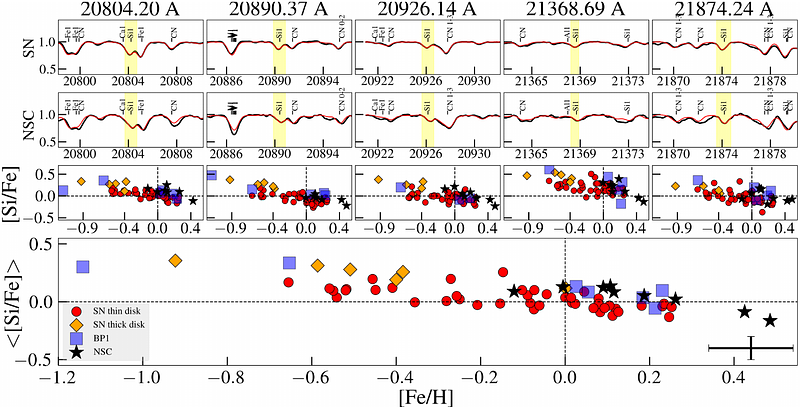
AbstractA chemical characterization of the Galactic Center is essential for understanding its formation and structural evolution. Trends of alpha-elements, such as Mg, Si, and Ca, serve as powerful diagnostic tools, offering insights into star-formation rates and gas-infall history. However, high extinction has previously hindered such studies. In this study, we present a detailed chemical abundance analysis of M giants in the Milky Way's Nuclear Star Cluster (NSC), focusing on alpha-element trends with metallicity. High-resolution, near-infrared spectra were obtained using the IGRINS spectrograph on the Gemini South telescope for nine M giants. Careful selection of spectral lines, based on a solar-neighborhood control sample of 50 M giants, was implemented to minimize systematic uncertainties. Our findings show enhanced alpha-element abundances in the predominantly metal-rich NSC stars, consistent with trends in the inner bulge. The NSC stars follow the high-[alpha/Fe] envelope seen in the solar vicinity's metal-rich population, indicating a high star-formation rate. The alpha-element trends decrease with increasing metallicity, also at the highest metallicities. Our results suggest the NSC population likely shares a similar evolutionary history with the inner bulge, challenging the idea of a recent dominant star formation burst. This connection between the NSC and the inner-disk sequence suggests that the chemical properties of extragalactic NSCs of Milky Way type galaxies could serve as a proxy for understanding the host galaxies' evolutionary processes.