Energy Estimates Across Layers of Computing: From Devices to Large-Scale Applications in Machine Learning for Natural Language Processing, Scientific Computing, and Cryptocurrency Mining
Energy Estimates Across Layers of Computing: From Devices to Large-Scale Applications in Machine Learning for Natural Language Processing, Scientific Computing, and Cryptocurrency Mining
Sadasivan Shankar
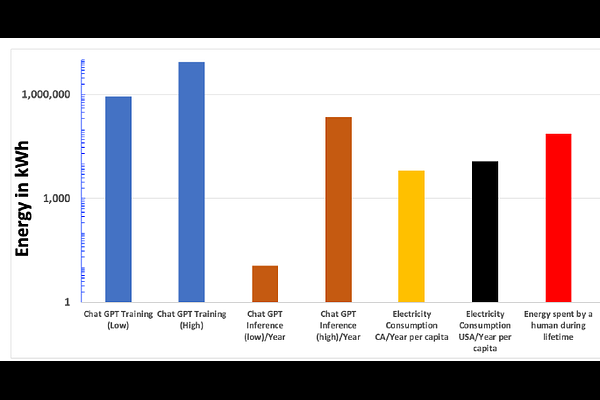
AbstractEstimates of energy usage in layers of computing from devices to algorithms have been determined and analyzed. Building on the previous analysis [3], energy needed from single devices and systems including three large-scale computing applications such as Artificial Intelligence (AI)/Machine Learning for Natural Language Processing, Scientific Simulations, and Cryptocurrency Mining have been estimated. In contrast to the bit-level switching, in which transistors achieved energy efficiency due to geometrical scaling, higher energy is expended both at the at the instructions and simulations levels of an application. Additionally, the analysis based on AI/ML Accelerators indicate that changes in architectures using an older semiconductor technology node have comparable energy efficiency with a different architecture using a newer technology. Further comparisons of the energy in computing systems with the thermodynamic and biological limits, indicate that there is a 27-36 orders of magnitude higher energy requirements for total simulation of an application. These energy estimates underscore the need for serious considerations of energy efficiency in computing by including energy as a design parameter, enabling growing needs of compute-intensive applications in a digital world.