Swift/XRT monitoring of the orbital and superorbital modulations in 4U 1909+07
Swift/XRT monitoring of the orbital and superorbital modulations in 4U 1909+07
P. Romano INAF/OAB, H. I. Cohen CUA CSST Uni. Maryland NASA GSFC, E. Bozzo Univ. Geneve INAF/OAB, N. Islam CSST Uni. Maryland NASA GSFC, A. Lange GWU CSST Uni. Maryland NASA GSFC, R. H. D. Corbet CRESST and CSST NASA GSFC Maryland ICA, B. Coley Howard Univ CRESST, K. Pottschmidt Uni. Maryland CRESST
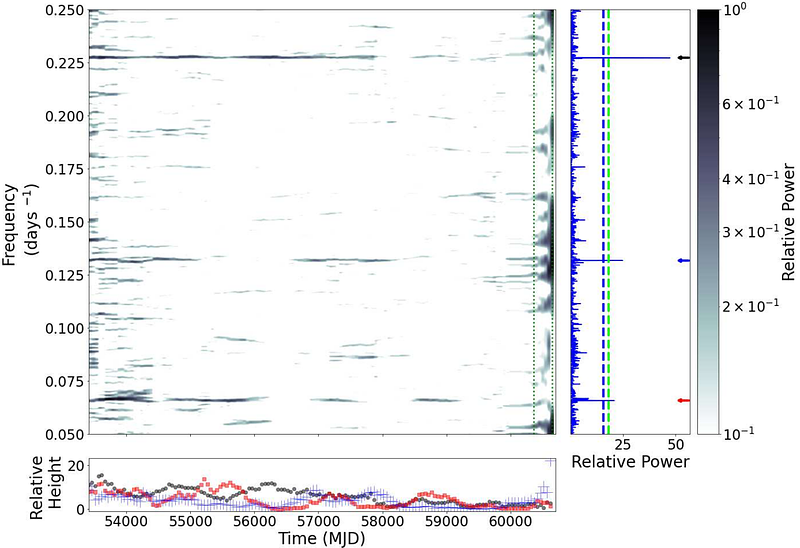
AbstractWe report on an observational campaign performed with Swift/XRT on the wind-fed supergiant X-ray binary 4U 1909+07 to investigate the nature of the orbital and superorbital modulation of its X-ray emission. A total of 137 XRT observations have been carried out, summing up to a total effective exposure time of 114 ks and covering a total of 66 orbital and 19 superorbital cycles of the source. The XRT data folded on the orbital period of the source confirmed and improved the previously reported variability in intensity and absorption column density, which can be ascribed to the neutron star accreting from the wind of its B supergiant companion across a fairly circular orbit. The XRT data folded on the superorbital period did not provide evidence of significant variations in either the absorption column density and/or the power-law photon index. This may be due to a significant weakening of the superorbital modulation during the times when the XRT observations were carried out, as confirmed by the BAT dynamic power spectrum. We discuss the implications of these findings within the corotating interaction region model proposed to interpret the superorbital variability in wind-fed supergiant X-ray binaries.