Trenchcoat: Human-Computable Hashing Algorithms for Password Generation
Trenchcoat: Human-Computable Hashing Algorithms for Password Generation
Ruthu Hulikal Rooparaghunath, T. S. Harikrishnan, Debayan Gupta
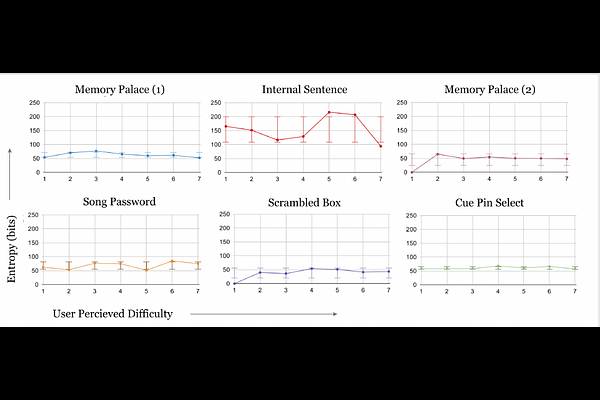
AbstractThe average user has between 90-130 online accounts, and around $3 \times 10^{11}$ passwords are in use this year. Most people are terrible at remembering "random" passwords, so they reuse or create similar passwords using a combination of predictable words, numbers, and symbols. Previous password-generation or management protocols have imposed so large a cognitive load that users have abandoned them in favor of insecure yet simpler methods (e.g., writing them down or reusing minor variants). We describe a range of candidate human-computable "hash" functions suitable for use as password generators - as long as the human (with minimal education assumptions) keeps a single, easily-memorizable "master" secret - and rate them by various metrics, including effective security. These functions hash master-secrets with user accounts to produce sub-secrets that can be used as passwords; $F_R($s$, w) \longrightarrow y$, takes a website $w$, produces a password $y$, parameterized by master secret $s$, which may or may not be a string. We exploit the unique configuration $R$ of each user's associative and implicit memory (detailed in section 2) to ensure that sources of randomness unique to each user are present in each master-secret $F_R$. An adversary cannot compute or verify $F_R$ efficiently since $R$ is unique to each individual; in that sense, our hash function is similar to a physically unclonable function. For the algorithms we propose, the user need only complete primitive operations such as addition, spatial navigation or searching. Critically, most of our methods are also accessible to neurodiverse, or cognitively or physically differently-abled persons. We present results from a survey (n=134 individuals) investigating real-world usage of these methods and how people currently come up with their passwords, we also survey 400 websites to collate current password advice.