The Distribution of Atomic Hydrogen in the Hosts Galaxies of FRBs
The Distribution of Atomic Hydrogen in the Hosts Galaxies of FRBs
Hugh Roxburgh, Marcin Glowacki, Clancy W. James, Nathan Deg, Qifeng Huang, Karen Lee-Waddell, Jing Wang, Manisha Caleb, Adam T. Deller, Laura N. Driessen, Alexa C. Gordon, J. Xavier Prochaska, Ryan M. Shannon, Dong Yang
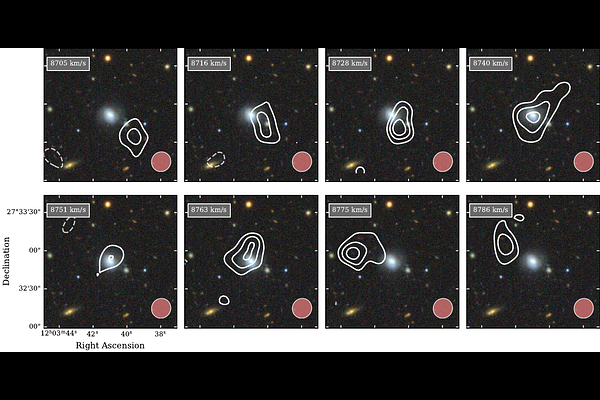
AbstractWe probe the atomic hydrogen (HI) emission from the host galaxies of fast radio bursts (FRBs) to investigate the emerging trend of disturbance and asymmetry in the population. Quadrupling the sample size, we detect 13 of 14 new hosts in HI, with the only non-detection arising in a galaxy known to be transitioning towards quiescence. With respect to typical local Universe galaxies, FRB hosts are generally massive in HI ($M_{HI}>10^9 M_\odot$), which aligns with previous studies showing that FRB hosts also tend to have high stellar masses and are star-forming. However, they span a broad range of other HI derived properties. In our independent sample of repeater hosts, we observe a statistically insignificant preference towards lower HI masses compared to non-repeater hosts, similar to the low-significance trend toward lower stellar masses previously reported. Using visual inspection alongside various asymmetry metrics, we identify four unambiguously settled host galaxies, demonstrating for the first time that a disturbed HI morphology is not a universal feature of FRB host galaxies. However, we find another six that show clear signs of disturbance, and three which require deeper, more targeted observations to reach a conclusion; this brings the confirmed ratio of disturbed-to-settled FRB hosts to 11:4. Given that roughly a 1:1 ratio is expected for random background galaxies of similar type, our observed ratio yields a p-value of 0.065. Unlike earlier indications based on smaller samples, this no longer crosses the conventional threshold for statistical significance, though is still near enough to hint at a legitimate excess of disturbance among FRB hosts. Thus, an even larger sample size of FRB hosts observed in HI is required to fully clarify whether the trend is genuine or still a consequence of low-number statistics - a sample that upcoming data releases are well positioned to provide.