A follow-up strategy enabling discovery of electromagnetic counterparts to highly-magnified gravitationally-lensed gravitational waves
A follow-up strategy enabling discovery of electromagnetic counterparts to highly-magnified gravitationally-lensed gravitational waves
Dan Ryczanowski, Jeff Cooke, James Freeburn, Benjamin Gompertz, Christopher P. Haines, Matt Nicholl, Graham P. Smith, Natasha Van Bemmel, Jielai Zhang
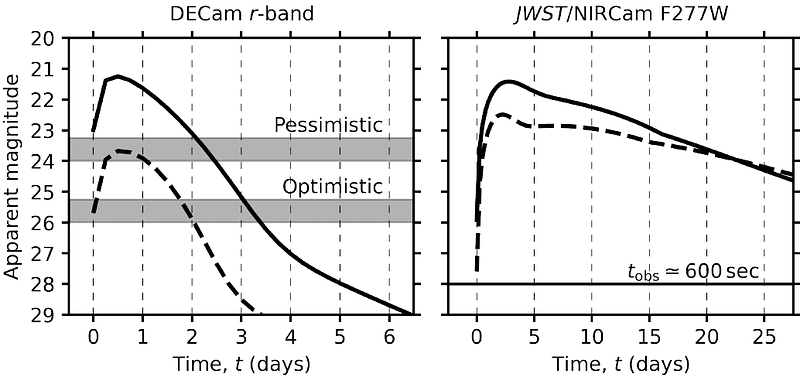
AbstractMaking an unambiguous detection of lensed gravitational waves is challenging with current generation detectors due to large uncertainties in sky localisations and other inferred parameter distributions. However, in the case of binary neutron star (BNS) mergers this challenge can be overcome by detecting multiple images of its lensed kilonova counterpart, simultaneously confirming the lensing nature of the event and locating it precisely - further enabling a wealth of lensed multimessenger science. Such a strategy demands answers to two key problems: 1) How can candidate lensed BNS events be identified fast enough to ensure the lensed kilonova is still detectable? 2) What is the most economical observing strategy on telescope time for following up candidate lensed events to discover lensed kilonovae? This article will discuss solutions to both points, specifically: how GW detections of progenitors in the $\sim$ 2.5 to 5 $M_\odot$ black hole "mass gap" can be interpreted as candidate lensed BNS events, giving evidence for lensing from just a single detection, and will present a strategy that can actively be employed for follow-up of such events in the O4 run of LVK and beyond.