SURE: A Visualized Failure Indexing Approach using Program Memory Spectrum
SURE: A Visualized Failure Indexing Approach using Program Memory Spectrum
Yi Song, Xihao Zhang, Xiaoyuan Xie, Songqiang Chen, Quanming Liu, Ruizhi Gao
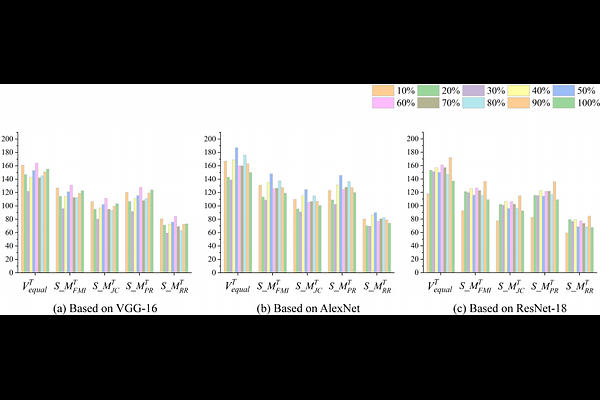
AbstractFailure indexing is a longstanding crux in software testing and debugging, the goal of which is to automatically divide failures (e.g., failed test cases) into distinct groups according to the culprit root causes, as such multiple faults in a faulty program can be handled independently and simultaneously. This community has long been plagued by two challenges: 1) The effectiveness of division is still far from promising. Existing techniques only employ a limited source of run-time data (e.g., code coverage) to be failure proximity, which typically delivers unsatisfactory results. 2) The outcome can be hardly comprehensible. A developer who receives the failure indexing result does not know why all failures should be divided the way they are. This leads to difficulties for developers to be convinced by the result, which in turn affects the adoption of the results. To tackle these challenges, in this paper, we propose SURE, a viSUalized failuRe indExing approach using the program memory spectrum. We first collect the run-time memory information at preset breakpoints during the execution of failed test cases, and transform it into human-friendly images (called program memory spectrum, PMS). Then, any pair of PMS images that serve as proxies for two failures is fed to a trained Siamese convolutional neural network, to predict the likelihood of them being triggered by the same fault. Results demonstrate the effectiveness of SURE: It achieves 101.20% and 41.38% improvements in faults number estimation, as well as 105.20% and 35.53% improvements in clustering, compared with the state-of-the-art technique in this field, in simulated and real-world environments, respectively. Moreover, we carry out a human study to quantitatively evaluate the comprehensibility of PMS, revealing that this novel type of representation can help developers better comprehend failure indexing results.