Hydrogen-poor Superluminous Supernovae with Bumpy Light Curves Powered by Precessing Magnetars
Hydrogen-poor Superluminous Supernovae with Bumpy Light Curves Powered by Precessing Magnetars
Biao Zhang, Long Li, Zi-Gao Dai, Shu-Qing Zhong
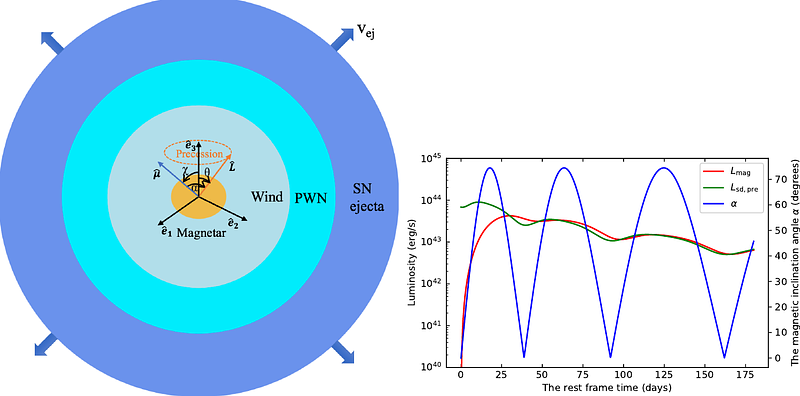
AbstractRecent observations and statistical studies have revealed that a significant fraction of hydrogen-poor superluminous supernovae (SLSNe-I) exhibit light curves that deviate from the smooth evolution predicted by the magnetar-powered model, instead showing one or more bumps after the primary peak. However, the formation mechanisms of these post-peak bumps remain a matter of debate. Furthermore, previous studies employing the magnetar-powered model have typically assumed a fixed magnetic inclination angle and neglected the effects of magnetar precession. However, recent research has shown that the precession of newborn magnetars forming during the collapse of massive stars causes the magnetic inclination angle to evolve over time, thereby influencing magnetic dipole radiation. In this paper, therefore, we incorporate the effects of magnetar precession into the magnetar-powered model to develop the precessing magnetar-powered model. Using this model, we successfully reproduce the multi-band light curves of 6 selected representative SLSNe-I with post-peak bumps. Moreover, the derived model parameters fall within the typical parameter range for SLSNe-I. By combining the precessing magnetars in SLSNe-I and long GRBs, we find that the ellipticity of magnetars is related to the dipole magnetic field strength, which may suggest a common origin for the two phenomena. Our work provides a potential explanation for the origin of post-peak bumps in SLSNe-I and offers evidence for the early precession of newborn magnetars formed in supernova explosions.