AT 2018dyk: tidal disruption event or active galactic nucleus? Follow-up observations of an extreme coronal line emitter with the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument
AT 2018dyk: tidal disruption event or active galactic nucleus? Follow-up observations of an extreme coronal line emitter with the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument
Peter Clark, Joseph Callow, Or Graur, Claire Greenwell, Lei Hu, Jessica Aguilar, Steven Ahlen, Davide Bianchi, David Brooks, Todd Claybaugh, Kyle Dawson, Axel de la Macorra, Peter Doel, Satya Gontcho A Gontcho, Gaston Gutierrez, Klaus Honscheid, Stephanie Juneau, Robert Kehoe, Theodore Kisner, Anthony Kremin, Martin Landriau, Laurent Le Guillou, Aaron Meisner, Ramon Miquel, John Moustakas, Ignasi Pérez-Ràfols, Eusebio Sanchez, Michael Schubnell, David Sprayberry, Gregory Tarlé, Benjamin A. Weaver, Hu Zou
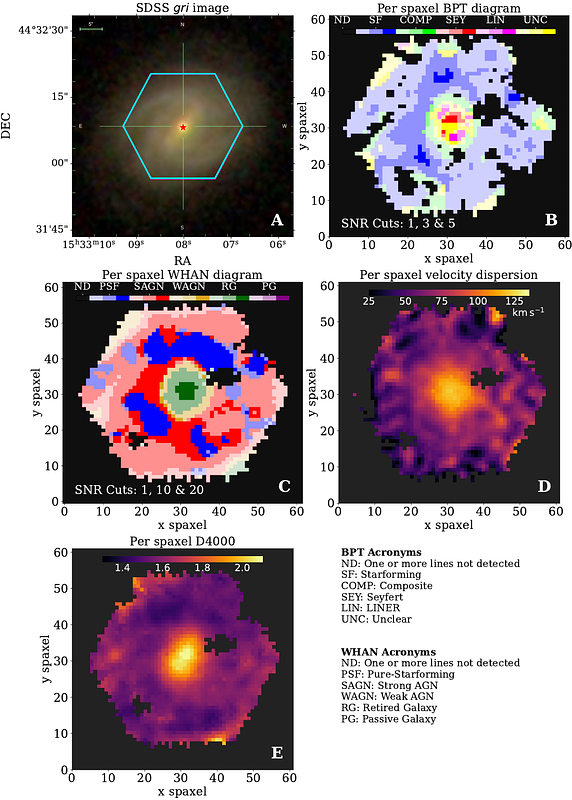
AbstractWe present fresh insights into the nature of the tidal disruption event (TDE) candidate AT 2018dyk. AT 2018dyk has sparked a debate in the literature around its classification as either a bona-fide TDE or as an active galactic nucleus (AGN) turn-on state change. A new follow-up spectrum taken with the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument, in combination with host-galaxy analysis using archival SDSS-MaNGA data, supports the identification of AT 2018dyk as a TDE. Specifically, we classify this object as a TDE that occurred within a gas-rich environment, which was responsible for both its mid-infrared (MIR) outburst and development of Fe coronal emission lines. Comparison with the known sample of TDE-linked extreme coronal line emitters (TDE-ECLEs) and other TDEs displaying coronal emission lines (CrL-TDEs) reveals similar characteristics and shared properties. For example, the MIR properties of both groups appear to form a continuum with links to the content and density of the material in their local environments. This includes evidence for a MIR colour-luminosity relationship in TDEs occurring within such gas-rich environments, with those with larger MIR outbursts also exhibiting redder peaks.