Supermassive black holes stripping a subgiant star down to its helium core: a new type of multi-messenger source for LISA
Supermassive black holes stripping a subgiant star down to its helium core: a new type of multi-messenger source for LISA
Aleksandra Olejak, Jakob Stegmann, Selma E. de Mink, Ruggero Valli, Re'em Sari, Stephen Justham
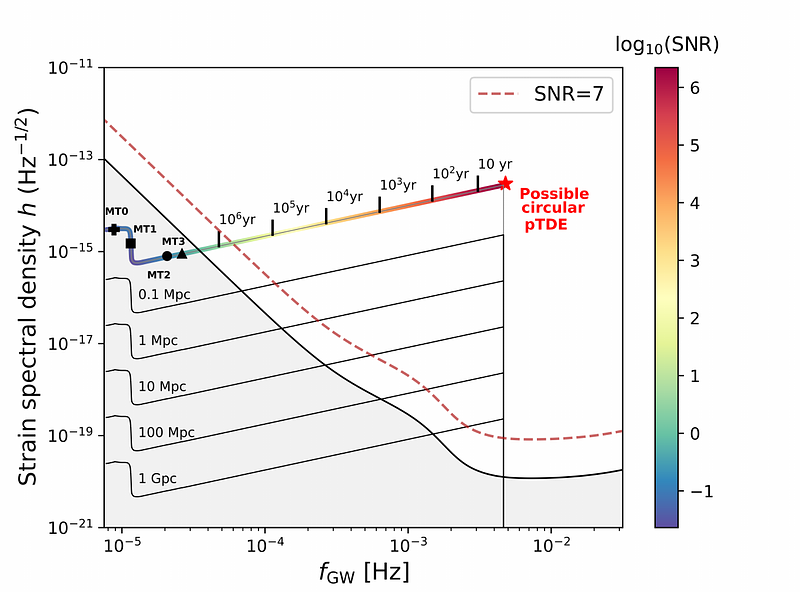
AbstractSome stars orbiting supermassive black holes (SMBH) are expected to undergo a gravitational-wave (GW)-driven inspiral and initiate mass transfer on nearly circular orbits. However, the stability and duration of such phases remain unexplored. In this work, we focus on the evolution of a low-mass, radiative-envelope subgiant star being stripped by an SMBH. We find that such systems can undergo a long-lasting, stable mass-transfer phase, even if none of the angular momentum of the transferred material returns to the orbit to counterbalance the GW-driven decay. We show an example where a 2 Msun subgiant is stripped before entering the LISA band and loses almost its entire hydrogen envelope. The remaining helium core undergoes a prolonged GW-driven inspiral, becoming a loud LISA source. If formed in our galaxy, the system would be detectable for several hundred thousand years, ultimately reaching extreme signal-to-noise ratios of a million. Hydrogen shell flashes in the residual envelope cause temporary radial expansions of the stripped star. As a result, a few additional phases of rapid mass transfer occur at orbital periods of 20 - 30 hours. Eventually, the core possibly undergoes circular partial tidal disruption at an orbital period of ~10 minutes, corresponding to a GW emission frequency of a few mHz. We estimate a chance of about 1% that such a detectable LISA source exists in our own galactic center. The loud final GW transient may lead to a few detections reaching as far as ~1 Gpc, including, e.g., the Abell clusters.