RBM39 degrader invigorates natural killer cells to eradicate neuroblastoma despite cancer cell plasticity
RBM39 degrader invigorates natural killer cells to eradicate neuroblastoma despite cancer cell plasticity
Singh, S.; Fang, J.; Jin, H.; Van de Velde, L.-A.; Wu, Q.; Cortes, A.; Morton, C.; Woolard, M.; Quarni, W.; Steele, J.; Connelly, J.; He, L.; Thorne, R.; Turner, G.; Confer, T.; Johnson, M.; Caufield, W.; Freeman, B.; Lockey, T.; Pruett-Miller, S.; Wang, R.; Davidoff, A.; Thomas, P.; Yang, J.
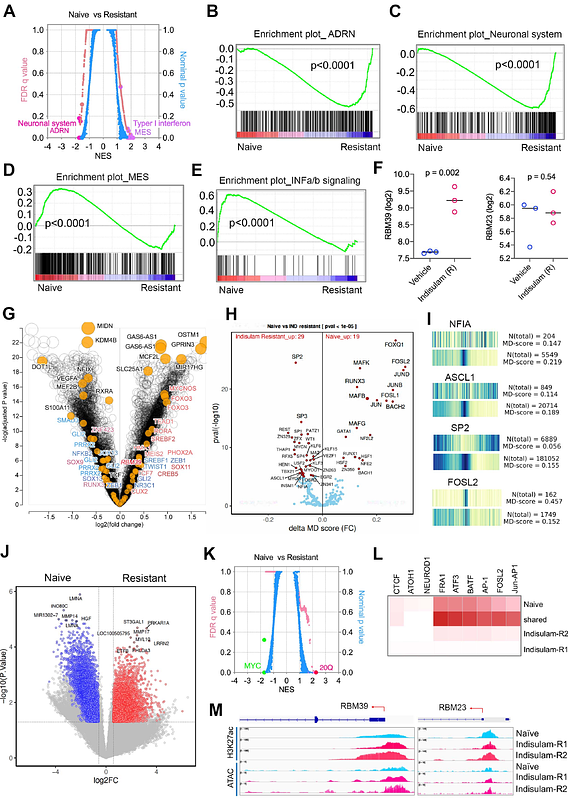
AbstractThe cellular plasticity of neuroblastoma is defined by a mixture of two major cell states, adrenergic (ADRN) and mesenchymal (MES), which may contribute to therapy resistance. However, how neuroblastoma cells switch cellular states during therapy remains largely unknown and how to eradicate neuroblastoma regardless of their cell states is a clinical challenge. To better understand the lineage switch of neuroblastoma in chemoresistance, we comprehensively defined the transcriptomic and epigenetic map of ADRN and MES types of neuroblastomas using human and murine models treated with indisulam, a selective RBM39 degrader. We showed that cancer cells not only undergo a bidirectional switch between ADRN and MES states, but also acquire additional cellular states, reminiscent of the developmental pliancy of neural crest cells. The lineage alterations are coupled with epigenetic reprogramming and dependency switch of lineage-specific transcription factors, epigenetic modifiers and targetable kinases. Through targeting RNA splicing, indisulam induces an inflammatory tumor microenvironment and enhances anticancer activity of natural killer cells. The combination of indisulam with ant-GD2 immunotherapy results in a durable, complete response in high-risk transgenic neuroblastoma models, providing an innovative, rational therapeutic approach to eradicate tumor cells regardless of their potential to switch cell states.